10.0.0.1 – 10.0.0.0.1 Admin Login
10.0.0.1 is a private IPv4 address. It is reserved for local networks. Many routers, such as Comcast/Xfinity and LPB Piso WiFi, set it as the default gateway. Private IP addresses, such as 10.0.0.1, are unique within a network. They let users access their router’s admin panel. Users can change settings like Wi-Fi passwords, SSID names, guest networks, and security protocols from there.
This IP address is often mistaken for 10.0.0.0.1. But that address is invalid. It will send users to a search engine. Always double-check the IP format to avoid errors.
How to Log In to 10.0.0.1 Admin Panel
Step 1: Confirm Your Router’s Default Gateway
Before attempting to log in, ensure your router uses 10.0.0.1 as its default gateway. Here’s how:
- Windows: Open Command Prompt > Type
ipconfig> Check Default Gateway. - Mac: Go to System Preferences > Network > Advanced > TCP/IP.
If the gateway isn’t 10.0.0.1, try alternatives like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1.
Step 2: Access the Login Page
- Open a web browser (Chrome, Firefox, etc.).
- Type
http://10.0.0.1or10.0.0.1in the address bar. - Press Enter to load the router’s login page.
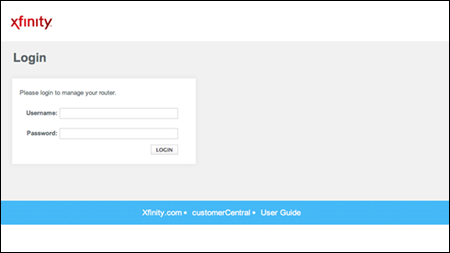
Step 3: Enter Default Username and Password
Most routers come with pre-configured credentials. Below are common defaults:
| Router Brand | IP address | Username | Password |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xfinity | 10.0.0.1 | admin | password |
| Cisco | 10.0.0.1 | admin | admin |
| Technicolor | 10.0.0.1 | user | user |
| Arris | 10.0.0.1 | admin | password |
| SMC | 10.0.0.1 | cusadmin | highspeed |
Note: Always change default credentials after setup to prevent unauthorized access.
Step 4: Configure Router Settings
Once logged in, you can:
- Change Wi-Fi password and SSID.
- Set up a guest network.
- Update firmware for security.
- Manage connected devices.
Common 10.0.0.1 Login Issues & Fixes
1. Admin Panel Won’t Load
- Cause: Incorrect IP address or slow connection.
- Fix:
- Verify the IP is 10.0.0.1 (not 10.0.0.0.1).
- Use a wired Ethernet connection for stability.
- Restart your router and device.
2. Forgotten Username/Password
- Fix:
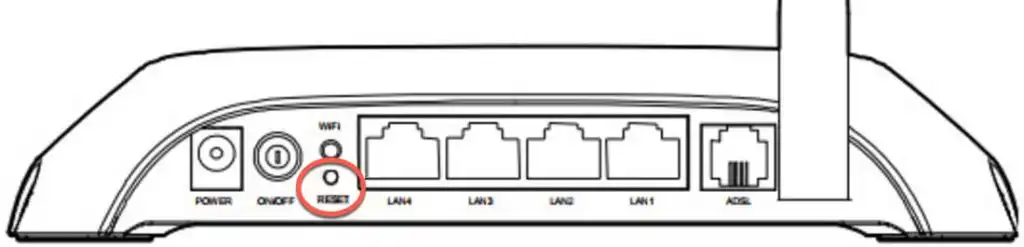
- Check the router’s label for default credentials.
- Perform a factory reset using the physical reset button (hold for 10–15 seconds).
3. “Unresponsive Gateway Device” Error
- Cause: Hardware glitches or outdated firmware.
- Fix:
- Power-cycle the router (unplug for 30 seconds).
- Update firmware via the admin panel.
4. Incorrect Client IP Assignment
- Cause: DHCP conflicts or automatic IP assignment errors.
- Fix:
- Assign a static IP to your device.
- Renew the IP lease via Command Prompt (
ipconfig /renew).
Advanced Tips for Managing 10.0.0.1 Router
Secure Your Network
- Change Default Login: Use a strong password with a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable WPA3 Encryption: Protects against brute-force attacks.
- Disable Remote Access: Prevents external tampering.
Optimize Wi-Fi Performance
- Channel Selection: Use tools like Wi-Fi Analyzer to find less congested channels.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritize bandwidth for streaming or gaming.
Monitor Connected Devices
Regularly review the list of connected devices in the admin panel to spot unauthorized users.
Why 10.0.0.1? Key Differences from Other IPs
While 10.0.0.1 is popular among Xfinity and LPB routers, other brands use different defaults:
- 192.168.1.1: Common for Netgear, Linksys.
- 192.168.0.1: Used by TP-Link, D-Link.
The 10.0.0.1 address falls under the Class A private IP range, which supports larger networks compared to Class C addresses (e.g., 192.168.x.x).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Conclusion
You can access your router’s admin panel at 10.0.0.1. This helps you solve issues, enhance security, and speed things up. Keep your firmware updated. Don’t share your login credentials. For ongoing problems, reach out to your ISP or the router manufacturer.
This guide helps you manage your home or office network easily. Save this article for easy reference when setting up in the future!

Janette Toral
Janette Toral is a Filipino digital media specialist, educator, and blogger known for her work in internet marketing and e-commerce education in the Philippines. She contributes to content on pisowifipausetime.ph and also writes practical guides related to IP Router configuration, local network management, and WiFi connectivity, contributing to Philippine online business and technology communities.
